As a wholesaler, you are critical to the success of the PVF industry. Complimenting your offering with pipe flanges means you can:
Pipe flanges connect piping and the components of a piping system such as valves, fittings, pipe with each other and specialty items using bolted connections and gaskets. They can be installed in several fashions including: welding, lapping or screwing.
There are several benefits to using a pipe flange including: it provides a secure connection between pipes, valves & other equipment; it allows for quick disassembly by providing installation or modification access points; and it increases the strength at the joint.
The application and type of flange determine the way in which the connection is made. Always consider the fluid being conveyed through a pipeline, the operating temperature, flange type, size, pressure class/rating and other specifications prior to installation. This ensures safety during installation and operation of the piping system.
A pipe flange has several components: a unique bolt pattern, connection type (e.g. socket weld, threaded, slip on, etc.) and face. They have varying bolt patterns that are based on the type of flange and its diameter. It is important to note that flanges do require a gasket to make the seal except for ring-type joint faces.
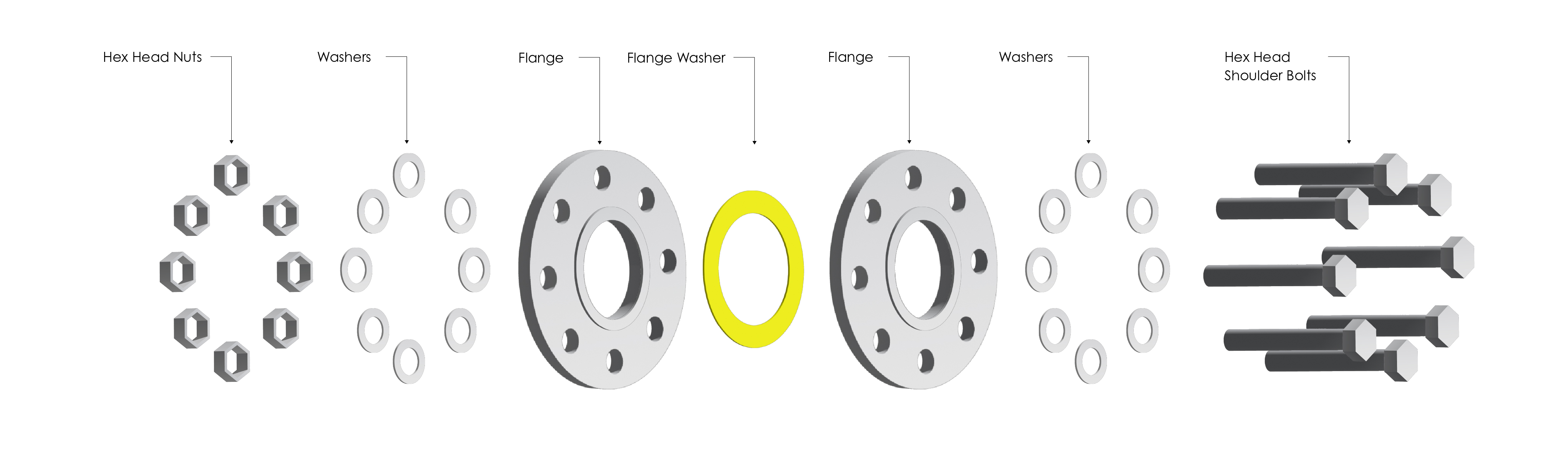
Pipe flanges can be manufactured from a casting (cast from a mold) or forging (using energy to change the shape of billet/ingot). They also come in various pressure ratings: 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500 and 2500 pounds. While they are available in several diameters, the larger flanges are available in the higher pressure class/rating.
Flanges also have several types of facing which include: flat face, ring-type joint, lap joint, tongue & groove and raised face. The facing is the area that is used to seal the flange.
| Industry | Flat-Full Face | Raised Face | Ring-Type Joint Face |
| Cast-Iron Equipment | X | ||
| High Pressure/High Temperature (up to 1382°F/750°C) | X | ||
| Low-Pressure Water Pipe Systems | X | ||
| Process Plants (Chemical, etc.) | X | ||
| Oil & Gas | X | X | |
| Valves | X |
The face itself can be serrated or smooth. There are several industries that traditionally require a specific type of facing.
There are several types of pipe flanges in a piping system; but there are 6 main types – blind, lap joint, slip on, socket weld, threaded and weld neck. Each of them has properties that determine their use in commercial, industriall and institutional applications. Always consult your project manager prior to installing any pipe flange into any application.
There are other types of flanges including: orifice, reducing, ductile iron backup, copper solder joint and many more.
| Type | Traditionally Used In |
| Blind |
|
| Lap Joint/Loose Ring |
|
| Slip-On/Hubbed |
|
| Socket Weld |
|
| Threaded |
|
| Weld Neck/Weld Bend |
|
Flanges are available in several alloys including: copper, brass, stainless steel, carbon steel, titanium, aluminum, superalloys, tool steel and alloy steel. Each alloy carries specific attributes:
| Alloy | Attributes |
| Alloy Steel |
|
| Aluminum |
|
| Brass |
|
| Carbon Steel |
|
| Copper |
|
| Stainless Steel |
|
| Super Alloys |
|
| Titanium |
|
| Tool Steel |
|



|
Can a stainless steel flange be put with carbon steel pipe? |
| Absolutely not, it would cause galvanic corrosion. Always consult your project team to ensure a proper, safe installation. |
| Does Merit's offering of pipe flanges come with flange protectors? |
| Yes. |
| Do ANSI Flanges come in raised face (RF) and flat-faced (FF)? |
| Yes, Merit's ANSI Flanges are raised face. The raised face can be machined off to make it the flat-faced style. |
| Can a flange be identified without stampings on the sides? |
| Yes, traditionally, the bolt dimensions, OD and thickness can identify which class the flange is. |
FAQ
LEARN MORE